Laryngoscopy
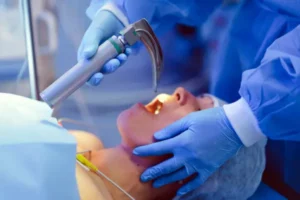 Laryngoscopy is a diagnostic procedure to examine the larynx known as voice box, and its surrounding areas including the vocal cords and throat.
Laryngoscopy is a diagnostic procedure to examine the larynx known as voice box, and its surrounding areas including the vocal cords and throat.
It can be classified by its method of performing, such as indirect laryngoscopy wherein a mirror and light are used, or direct laryngoscopy using a flexible or rigid scope with a camera.
⇒Indirect laryngoscopy: The doctor uses a small mirror and a bright light to look at the vocal cords. This is a simple outpatient procedure often done using numbing spray.
⇒Direct laryngoscopy: A laryngoscope, which is a tube with a light and camera, is inserted through the mouth or nose to get a direct, detailed view. This can be done in a clinic or operating room.
⇒Flexible laryngoscopy: A thin, flexible scope is often passed through the nose. This is a common and quick method.
⇒Rigid laryngoscopy: A rigid, stiff tube is inserted through the mouth. This is often performed under general anaesthesia in an operating room, and may be also be used for surgical interventions.
Uses of laryngoscopy:
⇒Diagnose the cause of hoarseness or voice related problems
⇒Investigate chronic cough or throat pain
⇒Check for issues like inflammation, blockages, or tumors in the larynx
⇒Find the cause of difficulty swallowing or noisy breathing
⇒Perform biopsies or remove small growths like vocal cord polyps
⇒Check for any injury to the larynx
Ready to Start Your Recovery Journey?
Our expert team is ready to help you achieve your rehabilitation goals and restore your quality of life.


